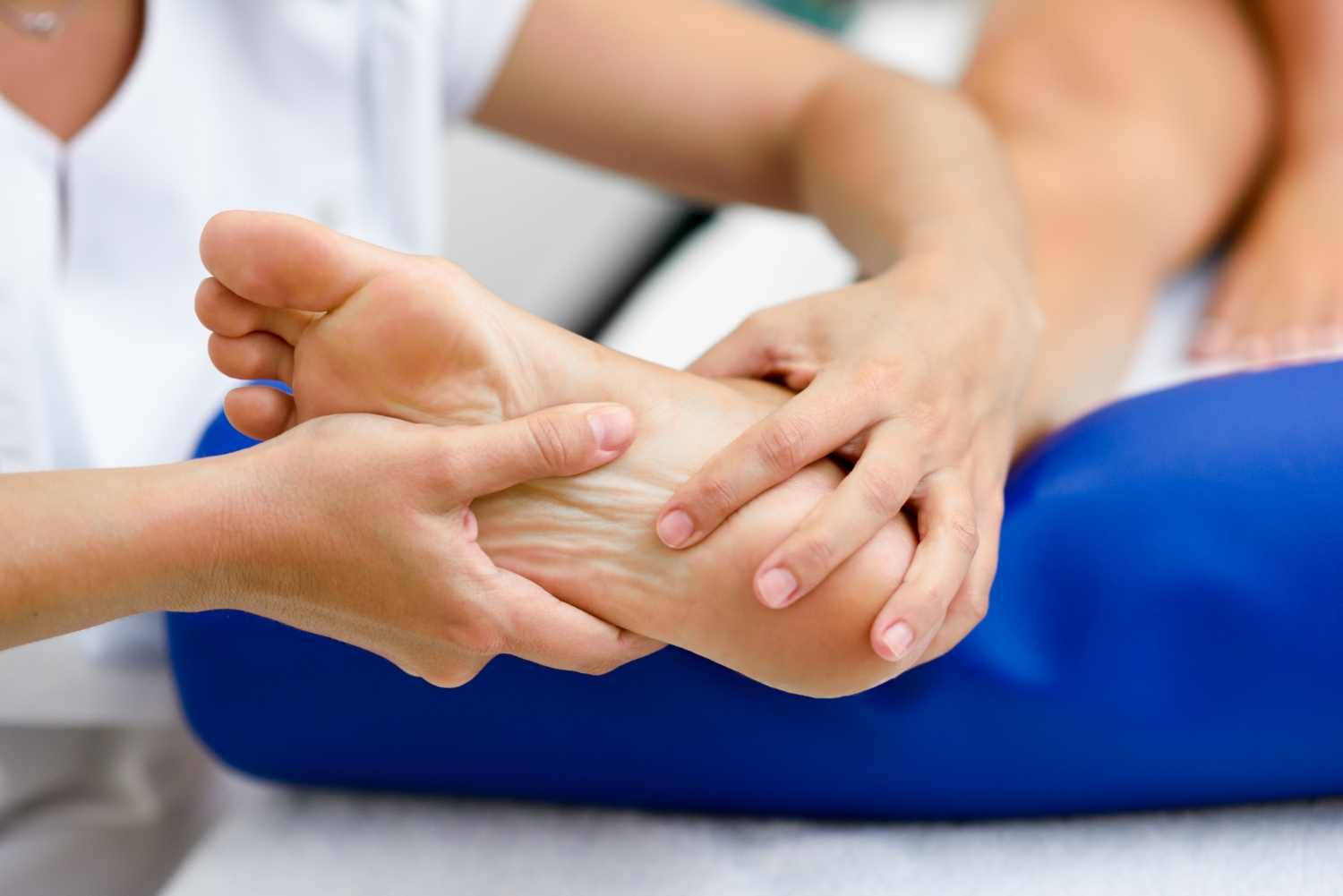
What is Peripheral Neuropathy?
The term peripheral neuropathy refers to nerve diseases that target a particular section of your nervous system. Peripheral neuropathy can be caused by various conditions, resulting in a diverse range of symptoms. Different body parts may be affected by peripheral neuropathy, depending on the circumstances.
The connection between the brain and spinal cord and the muscles, skin, and internal organs is facilitated by a complex network of peripheral nerves. Dermatomes are lines in the body where peripheral nerves emerge from the spinal cord. Usually, when a nerve is damaged, it impacts one or multiple dermatomes that can be traced to specific body regions. When the nerves are damaged, it hinders the flow of information between the brain and the body, which can result in muscle movement difficulties, loss of sensation in the arms and legs, and the occurrence of pain.
Symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy
Recognize the Signs: Understanding the Symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy
Book Now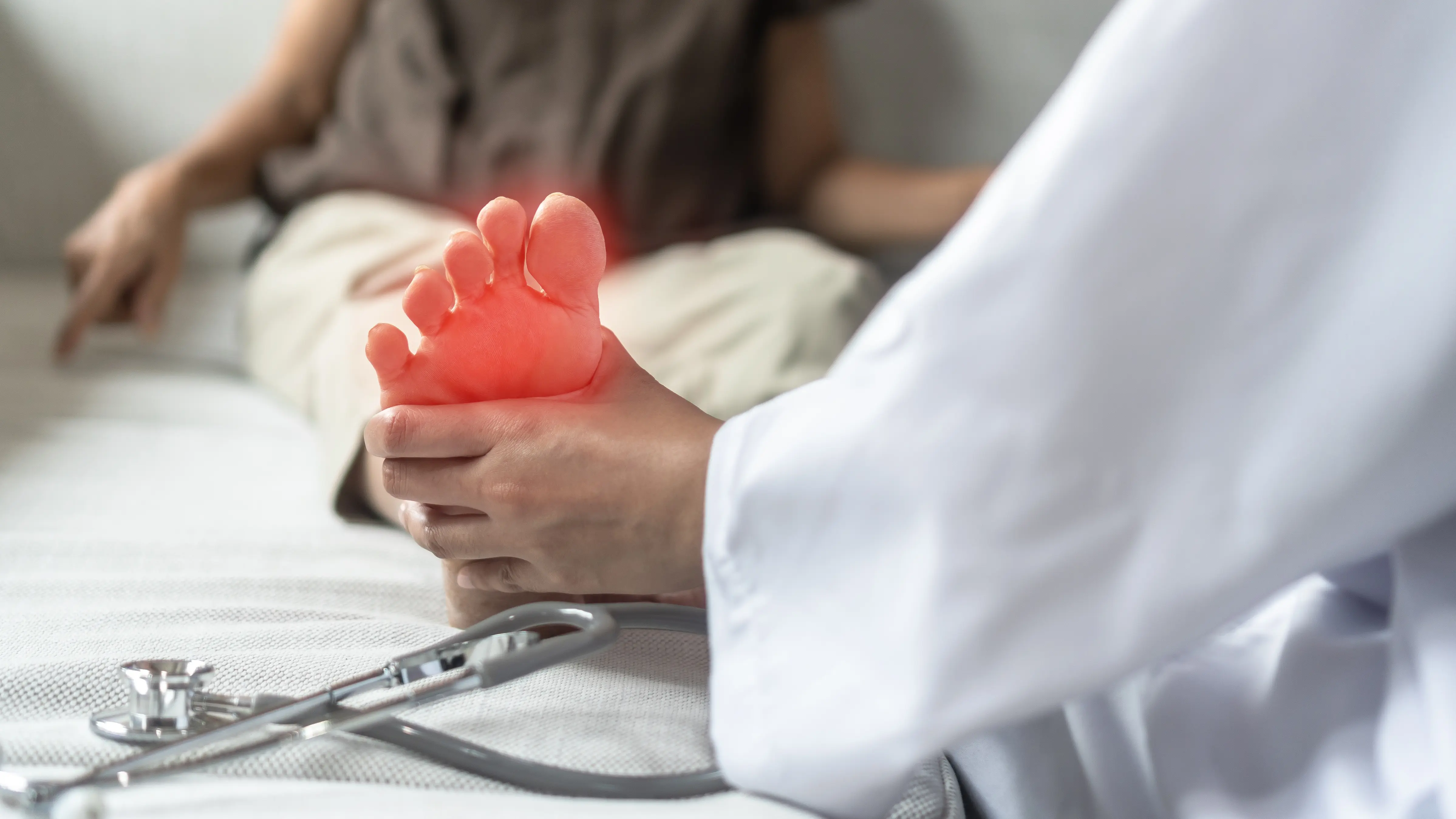
Ayurvedic Treatments for Peripheral Neuropathy in Kerala
Ayurveda views neuropathy as a harmful manifestation of disturbed vata. External factors, such as injury, can disrupt vata and hinder the transmission of nerve signals. Ayurveda refers to all nerve-related conditions as vata vyadhi. Nerve-related functions in the body are governed by the Vata dosha. The rise and fall of vata indicates poor health and manifests in distinct ways in the body. The ayurvedic treatment of peripheral neuropathy in Kerala involves calming vata. In certain instances, internal medications suffice, while hospitalisation is required for procedures like snehana, swedana, nasya, virechana, vasthi, and lepana.
Contact us to get the best Ayurvedic treatments for Peripheral Neuropathy in Kerala.
Ayurvedic Treatment
Ayur Bethaniya for Ayurvedic Treatment for Peripheral Neuropathy in Kerala
Book NowAyurveda focuses on addressing the underlying cause of illness, which in this case is the imbalance of doshas. In Ayurveda, the focus of treating Peripheral Neuropathy is to prevent myelin sheath degradation and aid in its regeneration. To achieve this, the body must first undergo panchakarma operations to remove all poisons at the cellular level.
Additional Ayurvedic remedies are offered to balance the doshas. Furthermore, yoga and meditation are used in Ayurvedic treatments to reduce stress, which is a crucial factor in the process. This course of therapy aids in the comprehensive reversal of peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes, hypertension, and inflammatory disorders can cause nerve damage, leading to over-excited senses and aggravated doshas. Burning from Pitta and tingling from an unbalanced Vata and Kapha. While balancing the three doshas can be challenging, at Ayur Bethaniya, we offer the best solution.
Patients suffering from neuropathy can benefit from our Panchakarma, particularly in complicated and chronic situations. Basti, Swedana, and Snehana are the primary treatments used in most cases, while Vamana and Virechana specifically aid in alleviating aggravated doshas. Ayur Bethaniya has been dedicated to delivering top-notch neuropathy care for several years, utilizing Ayurvedic medicines and panchakarma.
Feel free to contact us to get the best Ayurvedic treatments for Peripheral Neuropathy in Kerala.


